
A car may include several sensors such as an air-fuel ratio sensor, parking sensor, tire pressure monitor, oxygen sensor, etc. Each sensor is used for a specific purpose so that that vehicle runs at optimal efficiency.
Amongst these sensors, the oxygen sensor is considered to be the most important one. There are two types of Oxygen sensors, Upstream and Downstream. In this article, we will be discussing both these oxygen sensors in detail.
Upstream vs Downstream O2 Sensor
Let’s first have a look at how one is different from the other.
- Location
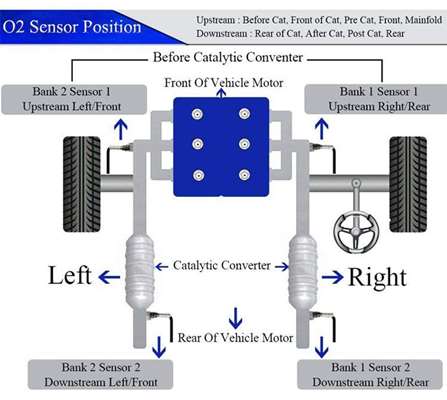
The location of an O2 sensor is relative to the catalytic converter. An upstream sensor is closer to the head, whereas a downstream one is present at the back of the catalytic converter(CAT).
In other words, an upstream is before the CAT and is also known as pre-CAT, whereas the downstream is after the CAT; therefore, it is known as post-CAT.
Another important factor that you must consider is to determine Bank One And Bank Two. To determine these respective banks, you will have to view the picture of your vehicle’s firing order. In the picture, whichever Bank contains cylinder 1 is Bank 1, whereas the other either has or doesn’t have cylinder two will be Bank 2.
- Working difference
As far as the working of both sensors is concerned, upstream is amongst the main inputs for fuel control, whereas the downstream is for emissions and On-board Diagnostics (OBD).
The main function of an upstream sensor is to determine the amount of NOx coming out of the engine and adjust the fuel/air ratio accordingly. On the other hand, the downstream o2 sensor function is to determine whether the CAT is doing its job.
If we further look into their working, it can be said that upstream provides data for Air to Fuel ratio, whereas the downstream keeps track of the CAT’s status and ensures it is not clogged and still working.
When installed in a modern OBD2 vehicle, the downstream O2 sensor determines the working of the catalytic converter. In contrast, in OBD 2 and later, it ensures enough oxygen for an efficient catalytic process.
How to visually identify upstream vs. downstream O2 sensors?
New car enthusiasts question how we can identify an upstream and downstream O2 sensor. Now, an upstream, as well as downstream sensor both, have some aesthetic differences. Some common identity differences between the both are the following:
- They have different connections spots and are not interchangeable
- The tip of both the sensors is different
- Upstream is either present above or close to the catalytic converter, whereas downstream is either in the catalytic converter or after the catalytic converter
- Downstream has a long wiring sensor as compared to upstream
- Upstream is square, and downstream is round
Can I Use a Downstream Oxygen Sensor for Upstream?
You may be thinking, Can I use a downstream oxygen sensor for upstream? Then a simple answer to this question is No. You can not use downstream oxygen sensors for upstream because they have different part numbers and their connections are different; therefore, neither you can mix them nor interchange them.
Product Recommendations
Oxygen Sensor Dodge Ram
Bosch Oxygen Sensor, Original Equipment for Dodge Ram. See the latest price here.
O2 Sensor for Toyota Camry
Oxygen Air Fuel Sensor for Toyota Camry. See the latest price here.
O2 Sensor for Nissan Altima
O2 Oxygen Sensor for Nissan Altima. See the latest price here.
What are the Upstream and Downstream O2 Sensor Readings?
An important thing you must know about both the sensors is their readings. An oxygen sensor reads oxygen levels only; therefore, their voltage range is 0.10 – 0.90 volts. 0.10 volts indicates high oxygen levels, whereas 0.90 volts indicates low oxygen levels. If the fuel mix is correct they will be .30-.70v, the sweet spot is .45v
Since the downstream sensor comes after the catalytic converter, it sees cleaned exhaust; therefore, it must indicate lower voltage and high oxygen levels, whereas the upstream sensor must indicate high voltage and low oxygen low levels.
How to Tell If Upstream or Downstream O2 Sensor is Bad?
Identifying a bad sensor is very important because if any sensor goes bad and you overlook it, it may harm your vehicle’s engine.
To check whether the upstream sensor has gone bad, you will have to look for signs such as messed up power output, gas mileage, engine performance, and Air/Fuel ratio. Likewise, detecting bad downstream o2 sensors can prove to be complicated because it can only be identified with code. The only sign you would see of a bad downstream is that it throws code.
Which O2 Sensor Goes Bad First Upstream or Downstream?
After our detailed discussion, a question that may arise in your mind is which sensor goes bad first. Now usually, it is said that the upstream sensor goes bad first. But if we talk in general, the main (upstream) o2 sensors go bad first from the crap that flows & burns through them (Gas).
Conclusion
The ending line is, l always keep a check on both of the oxygen sensors because if any of these goes bad, your car’s exhaust will start smelling like rotten eggs. Eventually, it could affect the overall performance of your car in the long run.
Related Article: How to Fix an Exhaust Manifold Leak



